Description
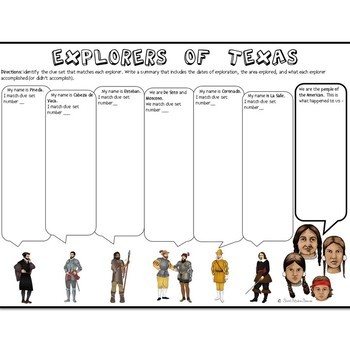
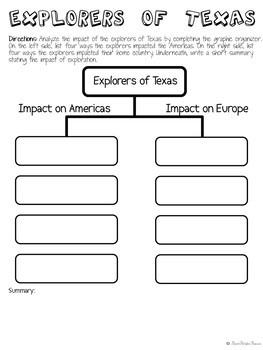
Explore the Conquistadors and Explorers of Texas with this fun activity. Students will be given a clue – they then have to decipher the symbols to find the explorer the clue represents. Students will then take notes on their Cartoon Notes and wrap up the activity with a tree map analyzing the impact of the explorers on the Americas.
With this resource, you will receive:
–Directions for how to conduct the activity.
– Content readings and clues on the major explorers of Texas including: Pineda, Cabeza de Vaca, Estevanico, Coronado, De Soto and Moscosco, and La Salle.
–Cartoon Notes Graphic Organizer for the explorers and their impact on the native peoples of the Americas.
⭐Please download the preview for more details. ⭐
*******************************************************************
TEXAS HISTORY TEKS
FOURTH GRADE
(2) History. The student understands the causes and effects of European exploration and colonization of Texas and North America. The student is expected to:
(A) summarize motivations for European exploration and settlement of Texas, including economic opportunity, competition, and the desire for expansion;
(B) identify the accomplishments and explain the impact of significant explorers, including Cabeza de Vaca; Francisco Coronado; and René Robert Cavelier, Sieur de la Salle, on the settlement of Texas;
SEVENTH GRADE
(2) History. The student understands how individuals, events, and issues through the Mexican National Era shaped the history of Texas. The student is expected to:
(B) identify important individuals, events, and issues related to European exploration of Texas such as Alonso Álvarez de Pineda, Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca and his writings, the search for gold, …
(21) Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including electronic technology. The student is expected to:
(A) differentiate between, locate, and use valid primary and secondary sources such as computer software, databases, media and news services, biographies, interviews, and artifacts to acquire information about Texas;
(B) analyze information by sequencing, categorizing, identifying cause-and-effect relationships, comparing, contrasting, finding the main idea, summarizing, making generalizations and predictions, and drawing inferences and conclusions;
(C) organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps;












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.